
About the Book
The first thing you will need to do to appreciate the sheer scale of the information contained in this book, is to look at the Table of Contents below. Then ask yourself where else could you find all of this information in a single, modern book, with fully worked examples, and with a practical guide to actual remedial equipment and materials used. Yet, despite the complexity of the topics covered, the author has concentrated on using the simplest analyses, and always uses worked examples, so that the design engineer can be confident he/she has the proper units and has completed his/her calculations correctly.
The wide ranging nature of this book means that if you could have only one book on the subject, then this would have to be it. It will be your go-to reference book and mentor.
If you want to be able to say that you know rock face and rock slope instability, then all you have to do is read this book from beginning to end and then put it on your bookshelf where you can find it easily. That's all.
CONTENTS
1. Introduction
2. Formation of the Solar System and the Earth
3. Composition of the planet Earth and its rocks
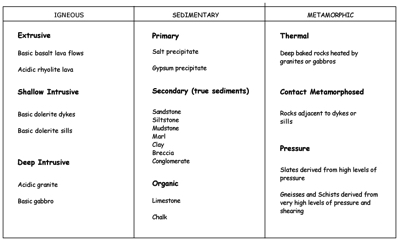
4. Fundamental Rock Types
4.1 Igneous Intrusive Rocks
4.2 Igneous Extrusive Rocks
4.3 Sedimentary Rocks
4.4 Metamorphic Rocks
5. Instability in Igneous Intrusive and Igneous Extrusive Rocks
5.1 Plutonic Intrusive Rocks
5.2 Concordant Minor Intrusive Rocks
5.3 Discordant Minor Intrusive Rocks
5.4 Extrusive Volcanic Lava Flows and Ash Rocks
6. Instability in Sedimentary Rocks
7. Instability in Metamorphic Rocks
8. Dip and Outcrop Recognition
9. The Mathematics of Rock Face Instability
9.1 The principles of acquisition, interpretation, and utilisation of
field and laboratory test data, as guided by Eurocode 7.
9.2 Problems associated with the practical applicability of Eurocode 7 to rockfall and rockface engineering and data anlysis and design.
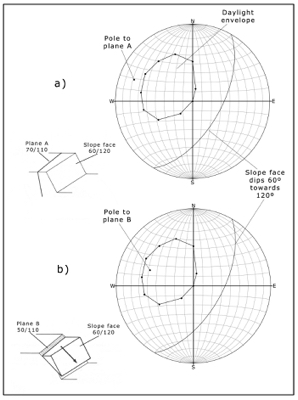
9.3 The representation of field data on stereo-net plots
9.4 Different types of rock movement
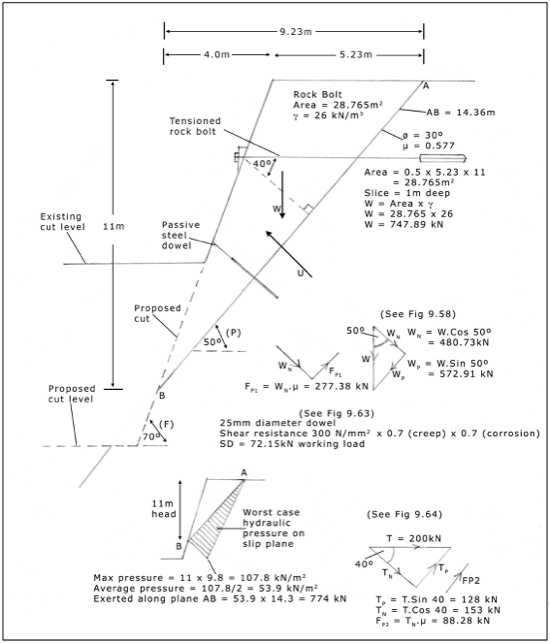
9.5 The mathematics of planar sliding
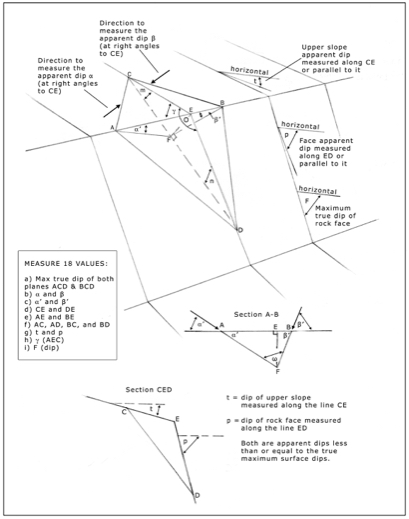
9.6 The Modular Mathematics of wedge sliding
9.6.1 Determination of the dimension of the wedge by
field measurement and calculation
9.6.2 Specification of the various physical restraining properties of the wedge on its
potential sliding plane's interfaces
9.6.3 Simple global analysis
9.6.4 Wedge 'Partition Method' with rigid response
9.6.5 Wedge 'Partition Method' with deformable response
9.7 Concepts of shared stress and cumulative strain on rock discontinuities
9.8 Mathematics of toppling rocks
9.8.1 Rocks standing alone
9.8.2 Rocks subject to external forces
9.8.3 The toppling of multiple rock groups
9.9 Mathematics of rolling rocks
9.10 Mathematics of falling rocks
9.11 Mathematics of bouncing rocks
9.12 Mathematics and principles of impact absorption
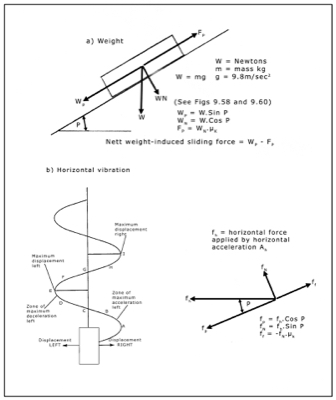
9.13 Seismic activity and its effects
10. Rock Control System Types A, B, C, & D
11. Type A. No Action Necessary
11.1 Stable outcome
11.2 Unstable outcome
12. Type B. Active Intervention Systems
12.1 Rock pins
12.2 Rock anchors
12.3 Hawsers
12.4 Meshes/nets
12.5 Sprayed concrete
12.6 Relocating rocks
13. Type C. Passive Intervention Systems
13.1 Wire fence barriers
13.2 Concrete and block wall barriers
13.3 Free-standing granular barriers
13.4 Reinforced soils barriers
13.5 Gabion barriers
13.6 Lateral diversion structures
13.7 Vertical diversion structures (shed tunnels)
13.8 Rock guidance nets
13.9 Catchment ditches
14. Type D. Remote Intervention Systems
14.1 Reducing water pressure
14.2 Reducing water ingress
14.3 Relocating affected structures
15. References
16. Bibliography
17. Geology Glossary
18. Physics Glossary
19. Appendix 1 Essential Equations
20. Appendix 2 The Roberts Rock Slope Hazard Classification System
21. Appendix 3 Rock Classifications
22. Appendix 4 The Use of the Camera and Mobile Telephone for Site Surveying
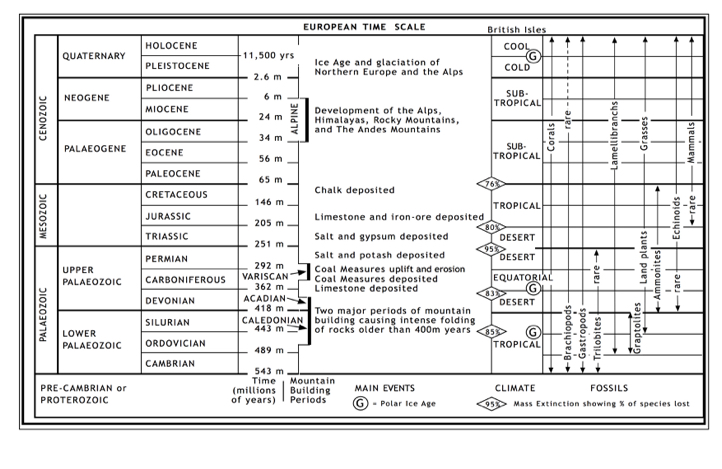
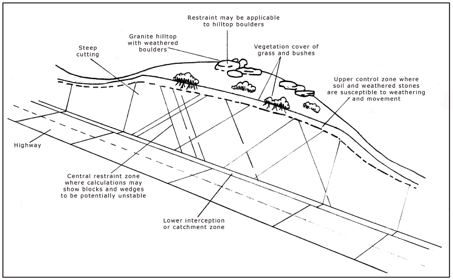
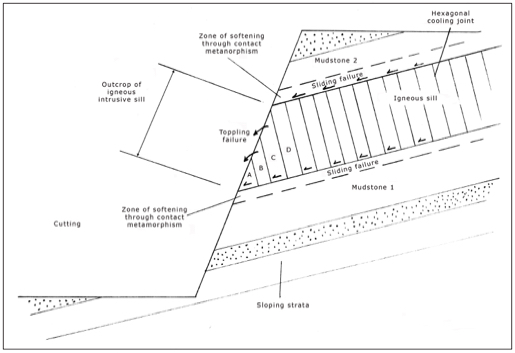
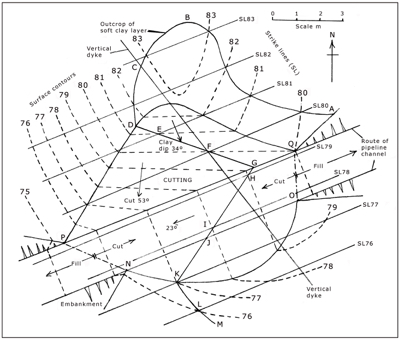
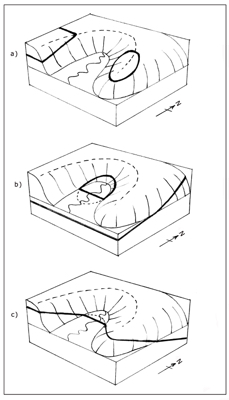
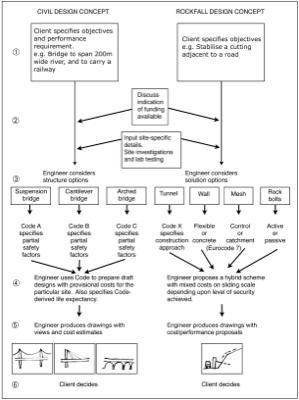
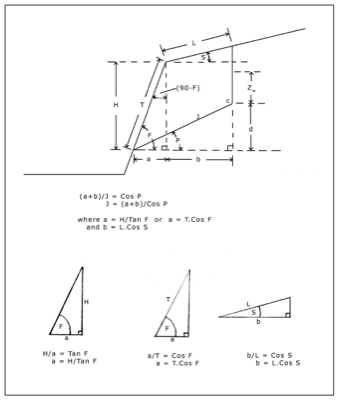
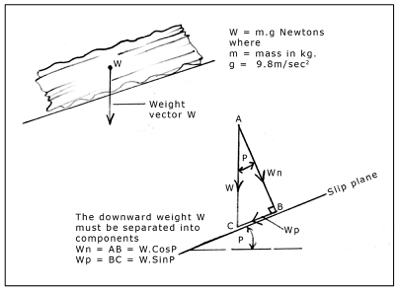
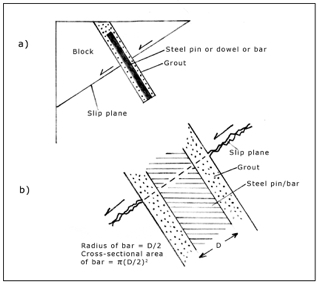
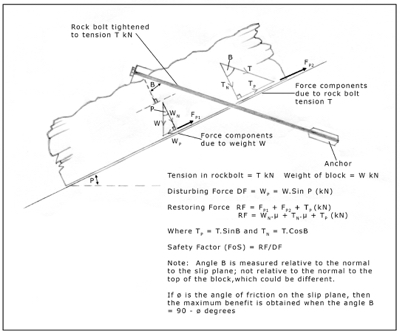
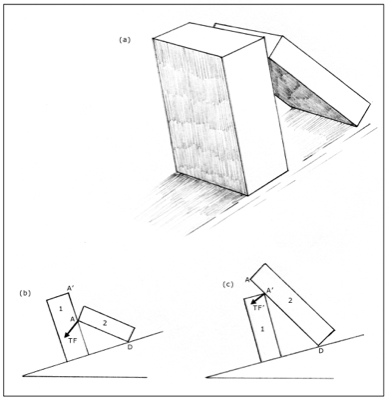
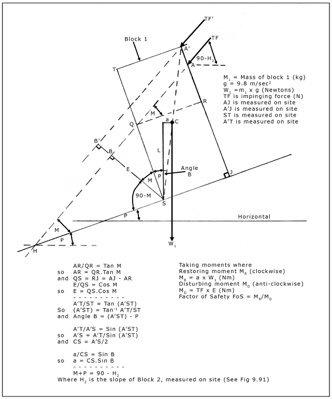
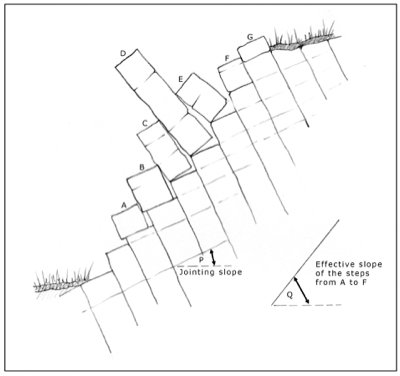
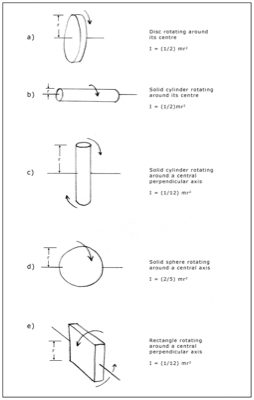
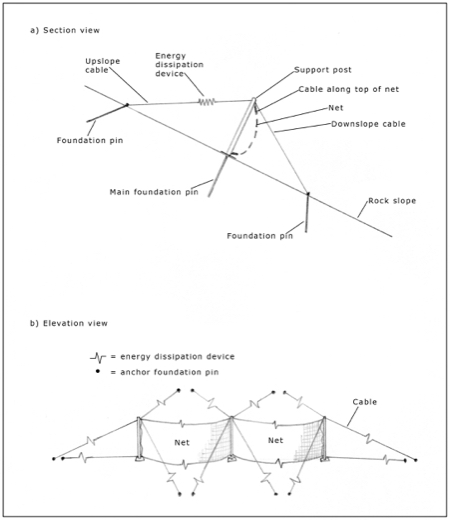
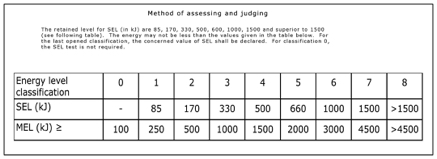
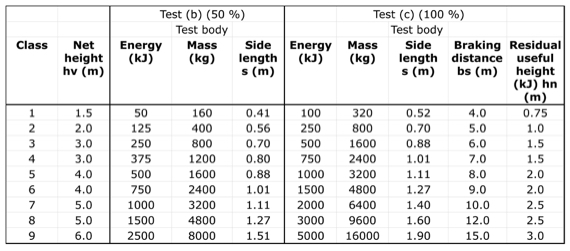
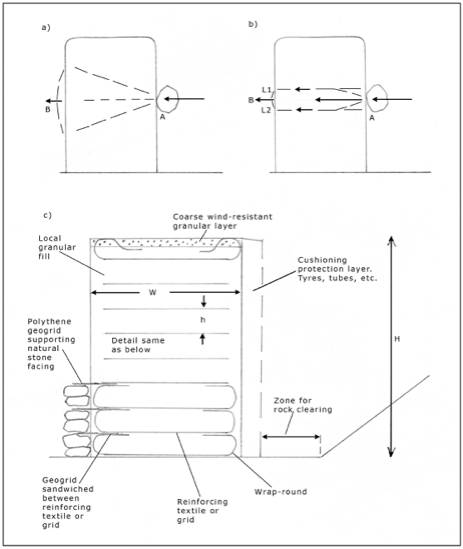
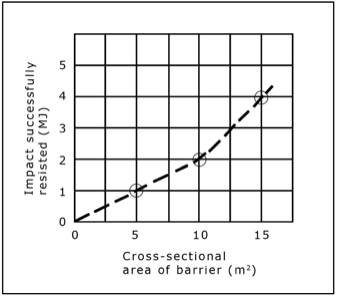
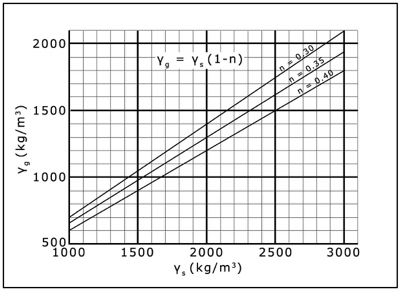

Would you like to have all the knowledge that is in these diagrams, as well as in the other 290 diagrams and illustrations in my book?
If so, just buy it!

Rock Slope Engineering
Peter Roberts
Rock Face Stability
Rock Mechanics
Reinforced Soil
Stereonet
Rock Slope Engineering
Prof Dr Peter Roberts
Rock Slope Engineering
The Geology and Mathematics of Rock Face Instability and Rockfall Control Design
Published by Russet Publishing. 2020. 538 US-letter-sized pages.
£69.80. Three copies are downloaded for you. One each for any combination of desktop computer, laptop, and/or tablet. Three PDF files will be sent, locked to either your personal or your work email address for your security. See our TERMS for necessary details.
This modern book is written for graduate civil engineers, engineering geologists, and geologists working in the geotechnical, highways, civil, and mineral extraction industries. It will also be useful for undergraduates studying for those professions.
The overall purpose of this book is to provide the engineer with the real, practical, information, technique, and maths to assess, design, and supervise rock stabilisation works on a day-to-day basis.
The great majority of the diagrams are drawn by Peter Roberts himself, thus reducing possible artistic error through the re-drawing process. The book contains working examples for all numerical procedures, and is Eurocode 7 aligned.
There is arguably no equally comprehensive, practical, or useful book available elsewhere.
ISBN 978-1-910537-38-1 Electronic EC7 Eurocode Version.
ISBN 978-1-910537-41-1 Electronic International Version.
HE LIKED IT—SEE IF YOU LIKE IT BEFORE YOU BUY
THIS BOOK IS ONLY AVAILABLE FROM RUSSET PUBLISHING
High definition electronic PDF version. 3 for the price of 1.
You can download to any three devices of your choice. For example, your work computer, your personal PC/laptop, your tablet or your smartphone. It's up to you.
Buy directly from us at Russest Publication
£69.80 VAT-free. (No P&P. No print and no postal delay.)
Add to cart and set quantity required on the cart page
For every one you order, we will send 3 for your personal use
THESE ARE SOME OF THE 290+ FIGURES AND COLOURED PHOTOGRAPHS FROM THE BOOK
WHEN YOU BUY AN EXPENSIVE BOOK, YOU NEED TO KNOW EXACTLY WHAT IS IN IT AND WHAT YOU ARE BUYING.
SCROLL DOWN AND READ ON:








By clicking "Add to Cart", you confirm that you have read and agreed to our terms of business and payment procedures.
Review by a senior staff member of one of the UK’s leading geotechnical consulting firms.
The book is very comprehensive and logically set out. From the theory of the formation of the solar system and the earth, through the different rock types and their weathering characteristics to the anatomy of different rock slopes and their instability, the book leaves the reader very aware of the complexities of the issues around rock slope engineering.
What is particularly impressive is that the book provides the reader with the practical means to survey and understand rock slope failure mechanisms and provides the tools for their effective remediation. Clear examples are provided at each step.
All in all, engineers with experience of this type of work will appreciate having this book at their finger tips and it is essential reading for anyone wanting to fully understand the elements of rock slope engineering. I wish I had access to this book at the beginning of my career and urge anyone serious in rock slope engineering to have a copy in their library.
I had no difficulty in downloading the book. I have already used it to aid in a couple of recent schemes and I have urged my team to make sure that they purchase a copy for themselves.
International Edition
EC7 Eurocode Edition

